




Next: Comparison between linear and
Up: Circular Motion of Point
Previous: Definitions of Physical Quantities
The Cross Product
Figure 2:
Cross Product
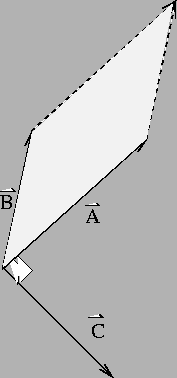 |
of two vectors 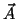 and
and 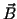 is
defined as the vector with magnitude:
is
defined as the vector with magnitude:
where 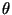 is the angle subtended by the two vectors. The
direction of the cross product
is the angle subtended by the two vectors. The
direction of the cross product 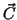 is always perpendicular to
both
is always perpendicular to
both 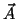 and
and 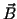 with the direction of the arrow
determined by the right hand rule: point the fingers of your
right hand from
with the direction of the arrow
determined by the right hand rule: point the fingers of your
right hand from  to
to 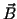 ,
and your thumb points along
the direction of the cross product
,
and your thumb points along
the direction of the cross product
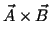 .
NOTE:
.
NOTE:
- The magnitude of the cross product has a geometrical
interpretation as the area of the parallelogram subtended by the
vectors
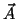 and
and 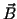 .
.
-
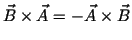 (i.e. they have
the same magnitude but point in opposite directions.
(i.e. they have
the same magnitude but point in opposite directions.
- If
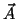 and
and 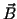 are parallel,
are parallel, 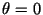 and the
cross product is zero.
and the
cross product is zero.
Torque about an axis O on a point mass due to a force 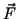 :
:
where 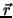 is the position vector of the mass relative to the
axis of rotation O.
is the position vector of the mass relative to the
axis of rotation O.
Angular Momentum about an axis O of a point ass m moving with
velocity 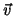 :
:
where 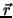 is the position of the mass relative to the axis and
is the position of the mass relative to the axis and
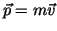 is its linear momentum.
is its linear momentum.





Next: Comparison between linear and
Up: Circular Motion of Point
Previous: Definitions of Physical Quantities
gabor@theory.uwinnipeg.ca
2001-01-05

![]() :
:
![]() :
: