 |
![]()
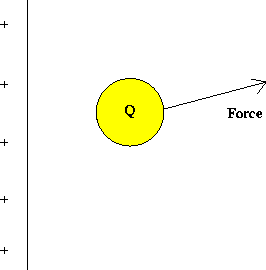
The electric field is a property of this fixed charge distribution; the force on a different charge Q' at the same point would be given by the product of the charge Q' and the same electric field. Note that the electric field at Q is always in the same direction as the electric force.
Because the force on a charge depends on the magnitude of the charges
involved and on the distances separating the charges, the electric
field varies from point to point, both in magnitude and direction.
By convention, the direction of the electric field at a point
is the direction of the force on a positive test charge placed at that
point. An example of the electric field due to a positive point charge
is given below.