



Next: Kinetic Energy and the
Up: Work and Energy
Previous: Work and Energy
Definition: The work done by an agent exerting a constant force
( 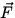 )
and causing a displacement (
)
and causing a displacement ( 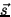 ) equals the magnitude of the
displacement,
s, times the component of
) equals the magnitude of the
displacement,
s, times the component of 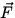 along the direction of
along the direction of 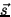 . In
Figure 5.1, the work done by
. In
Figure 5.1, the work done by 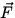 is:
is:
W = s Fcos  . .
|
|
| |
Figure 5.1:
Work
 |
Note:
- If
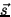 = 0
= 0  W = 0. (ie: no work is done when holding a
heavy box, or pushing against a wall).
W = 0. (ie: no work is done when holding a
heavy box, or pushing against a wall).
- W = 0 if
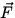

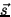 (ie: no work is done by carrying a
bucket of water horizontally).
(ie: no work is done by carrying a
bucket of water horizontally).
- The sign of W depends on the direction of
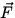 relative to
relative to 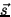 :
W > 0 when component of
:
W > 0 when component of 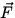 along
along 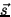 is in the same direction as
is in the same direction as
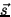 , and W < 0 when it is in the opposite direction. This sign is given
automatically if we write
, and W < 0 when it is in the opposite direction. This sign is given
automatically if we write  as the angle between
as the angle between 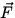 and
and 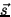 and write
W = Fscos
and write
W = Fscos  .
.
-
If
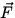 acts along the direction of
acts along the direction of 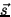 then W = Fs , since
cos
then W = Fs , since
cos  = cos 0 = 1.
= cos 0 = 1.
- Work is a scalar.
- The SI units of work are Joules (J) (1 Joule = 1
Newton
 meter). In
cgs units: 1 erg = 1 dyne
meter). In
cgs units: 1 erg = 1 dyne  cm.
cm.




Next: Kinetic Energy and the
Up: Work and Energy
Previous: Work and Energy
www-admin@theory.uwinnipeg.ca
10/9/1997
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()