Next: Circuits Up: Current and Resistance (Ch. Previous: Resistance
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Next: Circuits
Up: Current and Resistance (Ch.
Previous: Resistance
|
P = | (5) |
Electrical utilities normally bill on the basis of kilowatt-hours (kWh), which is the amount of energy the consumer has used in a given time period. One can convert kWh to J by the following formula:
1 kWh = 1000 Wh = 1000 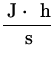 = 1000 = 1000 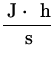 x 3600 = 3.6 x 106 J . x 3600 = 3.6 x 106 J .
| (6) |